If you’re considering raising ducks, then the Shetland Duck might be a great choice for you. This breed of duck is known for its unique quirks, distinctive characteristics, and fascinating origins. To help you learn more about Shetland Ducks, we’ve put together a comprehensive article that covers all the essential information you need to know. From their history and physical appearance to their nutritional needs and potential economic benefits, we have you covered.
The History and Origin of Shetland Ducks
The Shetland Duck, as you might have guessed from its name, is a breed that originally hail from the Shetland Islands in Scotland. The islands have long been known for their harsh and rugged environment, and as a result, the Shetland Duck evolved to be a tough and resilient breed. These ducks were originally bred for their meat and eggs, but over time, they became popular as pets and show animals.
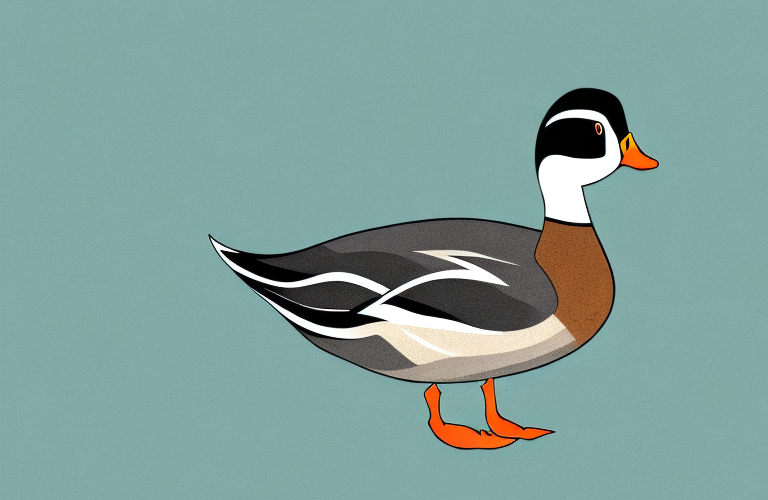
Shetland Ducks are a small breed, with males weighing around 2.5 kg and females weighing around 2 kg. They have a distinctive appearance, with a dark green head, white neck ring, and brown body. Their feathers are also unique, with a soft and fluffy texture that makes them popular for down production.
Today, Shetland Ducks are considered a rare breed, with only a few hundred individuals remaining worldwide. Efforts are being made to preserve the breed, including breeding programs and conservation initiatives. Despite their small numbers, Shetland Ducks continue to be valued for their hardiness, adaptability, and unique characteristics.
Appearance and Characteristics of the Shetland Duck
The Shetland Duck is a small to medium-sized breed that typically weighs between three to five pounds. They have a compact, muscular build and a distinctive wedge-shaped head. These ducks come in a range of different colors, including white, black, blue, and brown. One unique feature of the Shetland Duck is their small, upright tail feathers, which make them stand out from other breeds. Overall, they’re known for their hardiness, liveliness, and unique appearance.
In addition to their physical characteristics, the Shetland Duck is also known for their excellent egg-laying abilities. They can lay up to 200 eggs per year, which is impressive for a duck of their size. Their eggs are also known for their rich flavor and high nutritional value. Due to their hardiness and adaptability, the Shetland Duck is a popular choice for small-scale farmers and homesteaders who are looking for a low-maintenance, productive breed of duck.
The Unique Quirks of Shetland Ducks
One thing that sets Shetland Ducks apart from other breeds is their quirky personality. They’re known for being curious, friendly, and active birds that enjoy exploring and interacting with their owners. Some Shetland Ducks have even been known to bond with their human companions and follow them around like a loyal dog. They’re also known for being vocal birds, so if you live in a quiet area, you might want to consider another breed. Overall, the Shetland Duck is a charming and lovable bird with plenty of personality.
Another unique trait of Shetland Ducks is their adaptability to different environments. They can thrive in both rural and urban settings, making them a great choice for backyard farmers and city dwellers alike. They’re also hardy birds that can withstand harsh weather conditions, making them a good choice for those living in colder climates.
Shetland Ducks are also known for their delicious meat and eggs. Their meat is lean and flavorful, and their eggs are larger and richer in taste than those of other duck breeds. This makes them a popular choice for those who want to raise ducks for both meat and eggs.
The Best Environment for Raising Shetland Ducks
Shetland Ducks are adaptable and can thrive in a range of different environments. Whether you’re raising them on a farm, in a backyard, or in a suburban setting, there are a few key things you should keep in mind. Firstly, these ducks need access to water for swimming and cleaning. If you don’t have a pond or stream on your property, you can provide a small pool or water container. They also need a sheltered area to protect them from the elements, a dry and comfortable nesting area, and plenty of space to stretch their wings and exercise.
Another important factor to consider when raising Shetland Ducks is their diet. These ducks are omnivores and require a balanced diet of both plant and animal-based foods. You can provide them with a commercial duck feed or supplement their diet with fresh fruits, vegetables, and insects. It’s important to ensure that they have access to clean water and that their food is not contaminated with mold or bacteria.
Additionally, Shetland Ducks are social animals and thrive in groups. If you’re planning to raise these ducks, it’s recommended to keep at least two or three together. This will not only provide them with companionship but also help them regulate their body temperature during colder months. However, it’s important to monitor their behavior and ensure that there is no aggression or bullying within the group.
Feeding and Nutrition Tips for Shetland Ducks
Like all ducks, Shetland Ducks require a balanced diet that includes both grains and protein. You can feed them a commercial feed that’s specifically formulated for ducks, or you can create your own feed mix. Some good options for protein include mealworms, legumes, and soybeans, while grains like corn and barley are also great choices. It’s important to provide your ducks with fresh, clean water at all times, and to avoid feeding them bread or other processed foods that can be harmful to their health.
In addition to a balanced diet, Shetland Ducks also benefit from access to natural foraging opportunities. They enjoy grazing on grass, weeds, and other plants, as well as hunting for insects and other small prey. Providing your ducks with a safe and secure outdoor space where they can explore and forage can help keep them healthy and happy.
It’s also important to monitor your ducks’ weight and adjust their diet as needed. Overfeeding can lead to obesity and health problems, while underfeeding can result in malnutrition and poor egg production. Regularly checking your ducks’ body condition and consulting with a veterinarian or poultry expert can help ensure that they’re getting the right amount of food and nutrients.
Health Concerns for Shetland Ducks: Common Diseases and Preventive Measures
As with any animal, Shetland Ducks are susceptible to certain health issues and diseases. Some common concerns include respiratory infections, parasites, and bumblefoot. To keep your ducks healthy, it’s important to provide them with a clean living environment, regular check-ups with a veterinarian, and a balanced diet. You should also practice good biosecurity measures to prevent the spread of disease between your birds and other animals.
Another important aspect of maintaining the health of your Shetland Ducks is to ensure they have access to clean water at all times. Dirty water can lead to the growth of harmful bacteria and parasites, which can cause a range of health problems for your ducks. It’s also important to monitor your ducks for any signs of illness, such as lethargy, loss of appetite, or changes in behavior. Early detection and treatment of health issues can help prevent them from becoming more serious and potentially life-threatening.
Breeding and Incubation Techniques for Shetland Ducks
If you’re interested in breeding Shetland Ducks, there are a few things you should know. These ducks reach sexual maturity at around six months old and can lay around 100 to 150 eggs per year. To incubate their eggs, you’ll need a reliable incubator and a temperature-controlled environment. The incubation period typically lasts around 28 days, and once the eggs have hatched, you’ll need to make sure the chicks are kept warm and dry. It’s also important to handle your ducklings gently and to provide them with a balanced diet to help them grow strong and healthy.
When it comes to breeding Shetland Ducks, it’s important to keep in mind that they are a hardy breed that can adapt well to different environments. However, they do require a certain level of care and attention to ensure their health and well-being. This includes providing them with a clean and spacious living area, as well as regular access to fresh water and food.
In addition to proper care and nutrition, it’s also important to consider the genetics of your breeding stock. By selecting ducks with desirable traits such as good egg production, strong immune systems, and a calm temperament, you can improve the overall quality of your flock and increase your chances of success as a breeder.
Raising Shetland Ducks as Pets: Pros and Cons
If you’re considering raising Shetland Ducks as pets, there are a few pros and cons to keep in mind. On the positive side, these ducks are friendly, sociable, and entertaining to watch. They’re also relatively low maintenance and easy to care for. However, they can be noisy, messy, and require a certain level of space and attention. Additionally, if you live in an area with predators, you’ll need to take steps to protect your ducks from harm.
One of the benefits of raising Shetland Ducks is that they are excellent foragers. They will happily eat insects, snails, and other small creatures, which can help keep your yard or garden free of pests. They also enjoy grazing on grass and other vegetation, which can help keep your lawn trimmed and healthy.
On the downside, Shetland Ducks are not as common as other breeds, which can make them more difficult to find. They also have a tendency to become overweight if they are not given enough space to exercise and forage. This can lead to health problems, such as joint pain and heart disease. It’s important to provide your ducks with plenty of room to move around and access to fresh water and nutritious food.
The Economic Potential of Raising Shetland Ducks
Finally, if you’re considering raising Shetland Ducks for their meat or eggs, there are certainly some potential economic benefits. These ducks are known for their high-quality meat and eggs, and can be sold at a premium price compared to other breeds. Additionally, if you choose to raise ducks for meat, you can also sell the feathers and down for additional income. Of course, there are also expenses associated with raising ducks, such as feed, housing, and veterinary care, so it’s important to do your research and crunch the numbers before you get started.
Another potential economic benefit of raising Shetland Ducks is their ability to forage for food. Unlike other breeds that require a lot of supplemental feed, Shetland Ducks are excellent foragers and can find much of their own food in a pasture or yard. This can significantly reduce the cost of feed and increase your profit margin. Additionally, if you choose to sell your ducks or their products at a local farmers market or directly to consumers, you can build a loyal customer base and charge even higher prices for your high-quality, locally-raised products.
Comparing the Shetland Duck to Other Popular Duck Breeds
While the Shetland Duck is certainly a unique and captivating breed, it’s always worth comparing them to other popular duck breeds to see their similarities and differences. Some breeds that are often compared to the Shetland Duck include the Muscovy Duck, the Mallard, and the Pekin Duck. Each of these breeds has its own distinctive characteristics, so it’s important to do your research and choose the breed that suits your needs and preferences best.
One of the main differences between the Shetland Duck and the Muscovy Duck is their size. Muscovy Ducks are typically larger and heavier than Shetland Ducks. Additionally, Muscovy Ducks are known for their unique appearance, with red, warty skin around their eyes and beaks. Mallards, on the other hand, are a wild duck species that are commonly found in ponds and lakes. They are smaller than both Shetland and Muscovy Ducks and have distinctive green heads and yellow bills. Pekin Ducks, also known as Long Island Ducks, are a domesticated breed that are commonly raised for meat production. They are larger than Shetland Ducks and have white feathers and orange bills.
Where to Buy or Adopt a Shetland Duck
If you’re interested in adding a Shetland Duck to your flock, there are a few different options for finding one. Many breeders specialize in Shetland Ducks and can be found online or at local bird shows. Additionally, you may be able to find Shetland Ducks at farm supply stores or through local classified ads. If you’re interested in adopting a rescue duck, there are also organizations that specialize in rescuing and rehoming ducks that need a new home.
Overall, the Shetland Duck is a fascinating and lovable breed that’s well worth considering if you’re looking to raise ducks. With their unique quirks, hardy nature, and high-quality meat and eggs, they offer a lot of benefits to farmers, homesteaders, and even pet owners. By following the tips and information provided in this article, you can ensure that your Shetland Ducks stay healthy and happy for years to come.
It’s important to note that Shetland Ducks require a bit more care than other breeds of ducks. They are prone to certain health issues, such as bumblefoot and respiratory infections, so it’s important to keep their living area clean and dry. Additionally, they need access to water for swimming and preening, as well as a balanced diet that includes plenty of protein and fresh greens. By providing your Shetland Ducks with the proper care and attention, you can enjoy their unique personalities and many benefits for years to come.