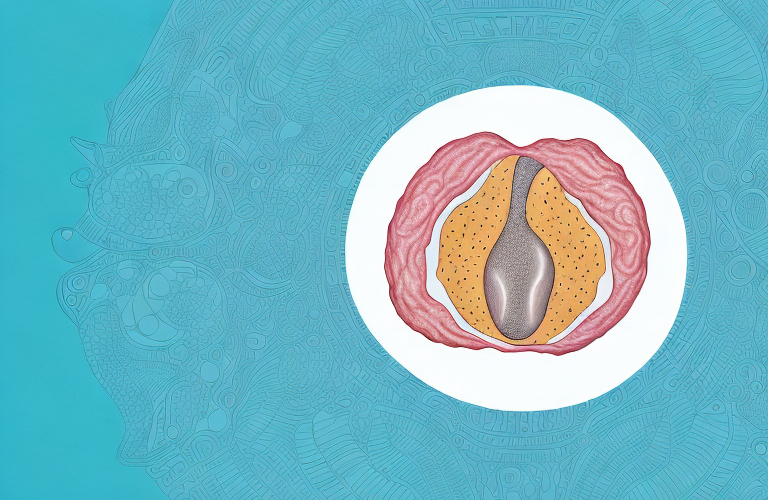
Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer that affects the vulva, which is the outer part of the female genitals. This type of cancer is relatively rare, with only around 6,000 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. However, it is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on a woman’s quality of life and overall health. In this article, we will provide an overview of vulvar cancer, including its symptoms, causes, treatment options, and more.
Understanding Vulvar Cancer: An Overview
Vulvar cancer is a type of cancer that affects the skin that covers the vulva. The vulva includes the external genitalia, such as the clitoris, labia, and vaginal opening. The most common type of vulvar cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which accounts for about 90% of cases. Other types of vulvar cancer include melanoma and adenocarcinoma.
Like other types of cancer, vulvar cancer can spread to other parts of the body if it is not treated early. However, with proper treatment, many women are able to successfully manage their cancer and maintain their quality of life.
It is important for women to be aware of the signs and symptoms of vulvar cancer, which may include itching, burning, pain, bleeding, or a lump or sore on the vulva. Regular gynecological exams can also help detect any abnormalities early on. Treatment options for vulvar cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches, depending on the stage and type of cancer.
What are the Symptoms of Vulvar Cancer?
The symptoms of vulvar cancer may include:
- A lump or mass on the vulva
- A patch of skin that looks different than the surrounding skin
- Bleeding or discharge from the vulva
- Pain or tenderness in the vulva
- Itching or burning in the vulva
- A sore that does not heal
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor right away. While these symptoms may be caused by other conditions, it is important to rule out vulvar cancer so that you can receive the appropriate treatment.
It is important to note that vulvar cancer is a rare type of cancer, accounting for only about 4% of all gynecologic cancers. However, it is still important to be aware of the symptoms and to seek medical attention if you experience any of them.
There are several risk factors that may increase a woman’s chances of developing vulvar cancer, including age, smoking, a weakened immune system, and a history of certain sexually transmitted infections. It is important to discuss any potential risk factors with your doctor and to undergo regular gynecologic exams to detect any potential issues early on.
Early Detection and Diagnosis of Vulvar Cancer
Like other types of cancer, early detection and diagnosis is key to successful treatment outcomes. Regular pelvic exams and Pap tests can help to detect vulvar cancer in its early stages, when it is easier to treat. If a suspicious area is found, your doctor may perform a biopsy to confirm whether or not it is cancerous.
It is important to note that not all cases of vulvar cancer present with noticeable symptoms. However, some common signs include itching, burning, or pain in the vulvar area, as well as changes in the color or thickness of the skin. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine if further testing is necessary.
What Causes Vulvar Cancer and Who is at Risk?
The exact causes of vulvar cancer are not known, but there are some factors that may increase a woman’s risk, including:
- Age (vulvar cancer is most commonly diagnosed in women over age 70)
- HPV infection
- Smoking
- Chronic skin conditions, such as lichen sclerosus or lichen planus
- A history of precancerous or cancerous lesions in the vulva or cervix
If you are at increased risk for vulvar cancer, it is important to talk to your doctor about screening and prevention strategies.
It is important to note that vulvar cancer is a rare type of cancer, accounting for only about 4% of all gynecologic cancers. However, it is still important to be aware of the risk factors and to take steps to reduce your risk.
Some steps you can take to reduce your risk of vulvar cancer include practicing safe sex, quitting smoking, and maintaining good hygiene. It is also important to attend regular gynecologic exams and to report any unusual symptoms, such as itching, burning, or bleeding, to your doctor.
Types of Vulvar Cancer: Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Melanoma, Adenocarcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of vulvar cancer, accounting for about 90% of cases. This type of cancer develops in the squamous cells that make up the skin that covers the vulva. Melanoma and adenocarcinoma are less common types of vulvar cancer.
While squamous cell carcinoma tends to grow slowly, melanoma and adenocarcinoma are more aggressive and can spread quickly to other parts of the body. Your treatment plan will depend on the type and stage of your cancer.
It is important to note that certain risk factors can increase your chances of developing vulvar cancer. These include smoking, having a weakened immune system, and being infected with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Regular gynecological exams and self-examinations can help with early detection and treatment of vulvar cancer.
Stages of Vulvar Cancer: How is it Classified?
Vulvar cancer is classified into four stages, from Stage I (early stage) to Stage IV (advanced stage). The stage of your cancer will depend on the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body. Knowing the stage of your cancer is important for guiding your treatment plan and helping you to understand the prognosis.
Stage I vulvar cancer is characterized by a tumor that is 2 centimeters or smaller and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body. Stage II vulvar cancer involves a tumor that is larger than 2 centimeters and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but has not spread to other parts of the body. Stage III vulvar cancer is when the tumor has spread to nearby tissues and organs, such as the urethra or anus, and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. Stage IV vulvar cancer is the most advanced stage, where the cancer has spread to distant organs, such as the lungs or liver.
Treatment Options for Vulvar Cancer: Surgery, Radiation Therapy, Chemotherapy
The treatment options for vulvar cancer may include:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and surrounding tissue
- Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to kill cancer cells
Your treatment plan will depend on the stage and type of your cancer, as well as your overall health and other factors. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended.
It is important to discuss the potential side effects and risks of each treatment option with your healthcare team. Surgery may cause pain, bleeding, and infection, while radiation therapy and chemotherapy may cause fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Your healthcare team can provide you with information on how to manage these side effects and improve your quality of life during treatment.
Supportive Care and Managing Side Effects during Vulvar Cancer Treatment
During treatment for vulvar cancer, you may experience a range of side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and pain. Your healthcare team can provide supportive care to help manage these side effects and maintain your quality of life. This may include medications, dietary changes, and other therapies, such as physical therapy or counseling.
It is important to communicate with your healthcare team about any side effects you are experiencing, as they may be able to adjust your treatment plan or provide additional support. In addition to medical interventions, self-care practices such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy diet can also help manage side effects and improve overall well-being during treatment.
Life After Treatment: Follow-Up Care and Survivorship for Vulvar Cancer Patients
After treatment for vulvar cancer, you will need to have regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare team to monitor for recurrence and manage any side effects. You may also be referred to supportive care services, such as survivorship programs or psychological counseling, to help you manage the emotional and physical impact of your cancer diagnosis.
It is important to note that follow-up care and survivorship for vulvar cancer patients may vary depending on the stage and type of cancer, as well as the individual’s overall health and treatment plan. Your healthcare team will work with you to develop a personalized follow-up care plan that meets your specific needs and goals. This may include regular physical exams, imaging tests, and blood work to monitor for any signs of recurrence. Additionally, your healthcare team may recommend lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and exercise, to help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and improve overall health and well-being.
Prevention Strategies for Avoiding Vulvar Cancer Risk Factors
While there is no surefire way to prevent vulvar cancer, there are some strategies that may help to reduce your risk, such as:
- Getting the HPV vaccine (which helps to protect against some of the strains of HPV that are linked to vulvar cancer)
- Quitting smoking
- Maintaining good hygiene (such as keeping the vulvar area clean and dry)
- Having regular pelvic exams and Pap tests, as recommended by your healthcare provider
It is also important to be aware of any changes in the vulvar area, such as itching, burning, or pain, and to report them to your healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment of any abnormalities can help to prevent the development of vulvar cancer.
Research Updates on Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Vulvar Cancer
The field of vulvar cancer research is constantly evolving, with new advances in diagnosis and treatment emerging all the time. For example, some studies are exploring the use of immunotherapy to help the body’s own immune system fight cancer cells. Other studies are looking at ways to improve the accuracy of cancer staging and diagnosis, such as using advanced imaging techniques to better visualize tumor size and location.
Additionally, there is ongoing research into the use of targeted therapies for vulvar cancer treatment. These therapies are designed to specifically target cancer cells, while minimizing damage to healthy cells. Another area of research is focused on identifying biomarkers that can help predict a patient’s response to certain treatments, allowing for more personalized and effective treatment plans.
Coping with a Diagnosis of Vulvar Cancer: Emotional Support and Resources
A diagnosis of vulvar cancer can be overwhelming, and it is important to have emotional and social support throughout your journey. Your healthcare team can provide resources and referrals to support groups, survivorship programs, and other organizations that can help you navigate the challenges of cancer treatment and recovery.
It is also important to take care of your mental health during this time. Consider seeking counseling or therapy to help you cope with the emotional impact of your diagnosis. Your healthcare team can provide recommendations for mental health professionals who specialize in working with cancer patients.
Conclusion: Raising Awareness about Vulvar Cancer and Empowering Women to Take Action
Vulvar cancer is a serious but treatable condition that affects thousands of women each year. By raising awareness about the risks and symptoms of vulvar cancer, we can empower women to take action and seek timely treatment if necessary. If you have any concerns about your vulvar health, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider right away.
It is also important to note that early detection is key in successfully treating vulvar cancer. Regular gynecological exams and self-examinations can help detect any abnormalities or changes in the vulvar area. Additionally, practicing safe sex and maintaining good hygiene can also reduce the risk of developing vulvar cancer. By taking these preventative measures and staying informed about vulvar health, we can work towards reducing the incidence and impact of this disease.