Recommended Daily Intake Of Magnesium
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies depending on age and gender. According to the National Institutes of Health, adult men should aim to consume between 400-420 mg/day, while women should consume between 310-320 mg/day. Pregnant and breastfeeding women require higher doses of magnesium to support fetal growth and milk production.
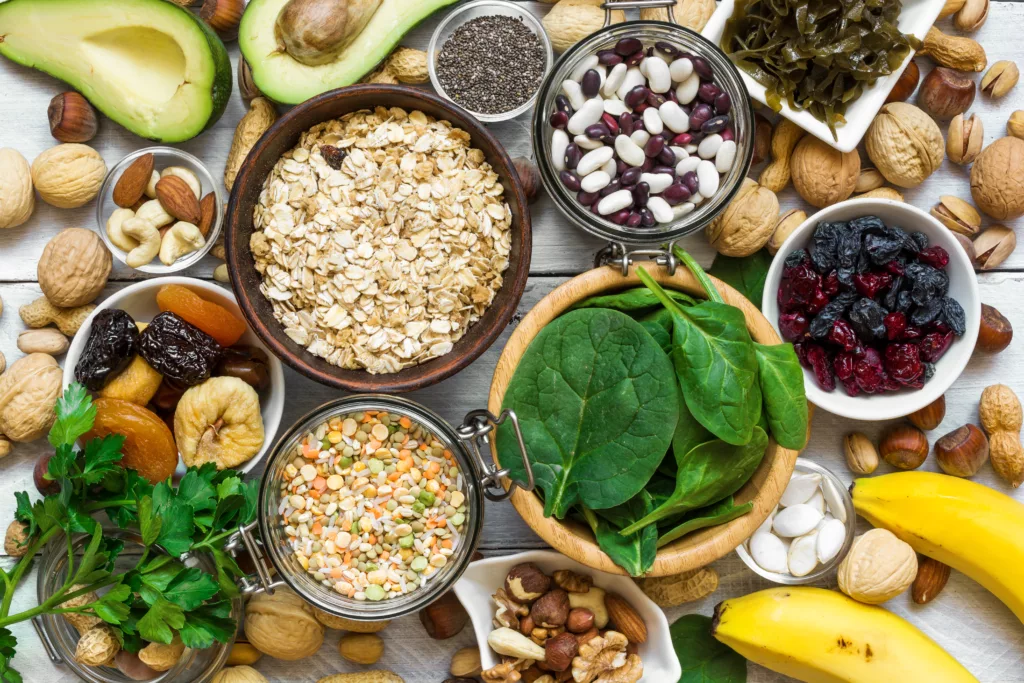

Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions. It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including energy production, protein synthesis, and muscle and nerve function. Magnesium also helps regulate blood sugar levels and blood pressure, and is important for bone health.
Despite its importance, many people do not consume enough magnesium in their diets. Common dietary sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. However, factors such as soil depletion, food processing, and certain medications can reduce the magnesium content of foods.
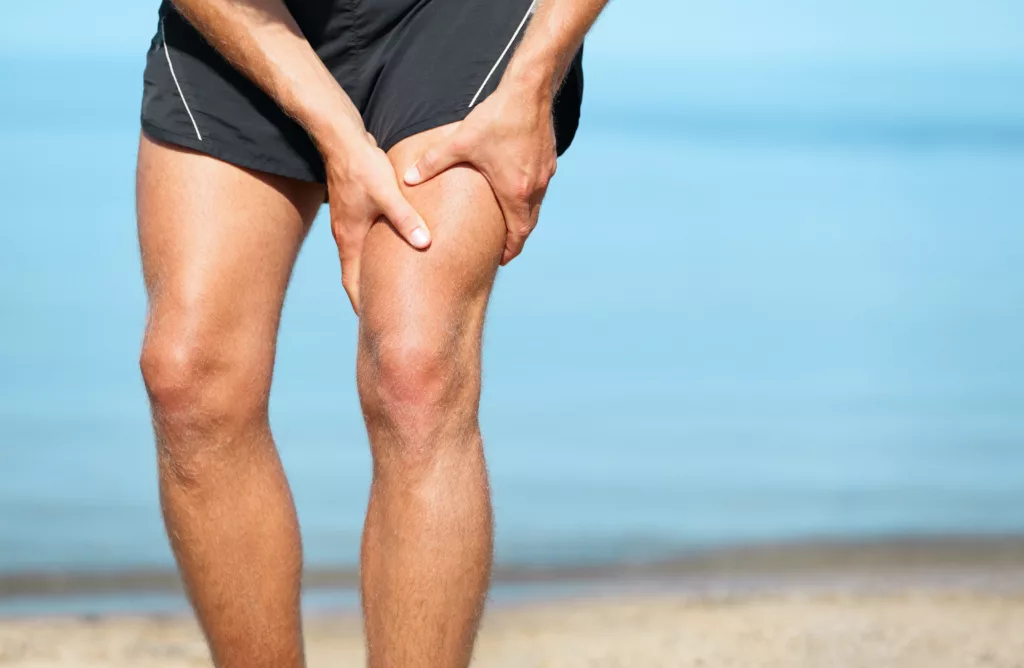

Magnesium Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Risks
A magnesium deficiency can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, and irregular heartbeat. Severe magnesium deficiency can cause seizures, numbness and tingling, and even personality changes. Several factors can contribute to a magnesium deficiency, including a diet lacking in magnesium-rich foods, certain medical conditions, and medications.

One of the most common causes of magnesium deficiency is a diet lacking in magnesium-rich foods. Foods that are high in magnesium include leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. However, many people do not consume enough of these foods on a regular basis, which can lead to a deficiency over time.
In addition to dietary factors, certain medical conditions can also contribute to a magnesium deficiency. These include gastrointestinal disorders that affect the absorption of nutrients, such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease. Kidney disease and diabetes can also increase the risk of magnesium deficiency, as can certain medications, such as diuretics and antibiotics.