Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the Corn Crake bird breed. In this article, we will explore various aspects of this fascinating bird, including its physical characteristics, habitat and distribution, life cycle and reproduction, diet and feeding habits, behavior and vocalizations, conservation status and threats, importance in ecosystems, interesting facts, identification and differentiation from similar bird species, conservation efforts, tips for birdwatching, the role of citizen science in monitoring populations, challenges faced by conservationists, success stories, and the future outlook for the conservation of the Corn Crake. So, let’s dive in and learn more about this remarkable bird.
Introduction to the Corn Crake bird breed
The Corn Crake (Crex crex) is a medium-sized bird species belonging to the rail family. It is known for its unique call, which resembles the sound of a rasping corn saw. The Corn Crake is mostly found in Europe, Asia, and Africa, particularly in grasslands, meadows, and wetlands. Its secretive nature and excellent camouflage make it a challenging bird to spot in the wild.
Despite its elusiveness, the Corn Crake plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems it inhabits. Understanding this bird’s characteristics and conservation status is essential for protecting its population and preserving biodiversity.
The Corn Crake is a migratory bird, spending its breeding season in Europe and Asia, and then migrating to Africa for the winter. During the breeding season, the male Corn Crake establishes its territory by calling loudly from a concealed spot in the vegetation. This call is not only used to attract females but also serves as a warning to other males to stay away.
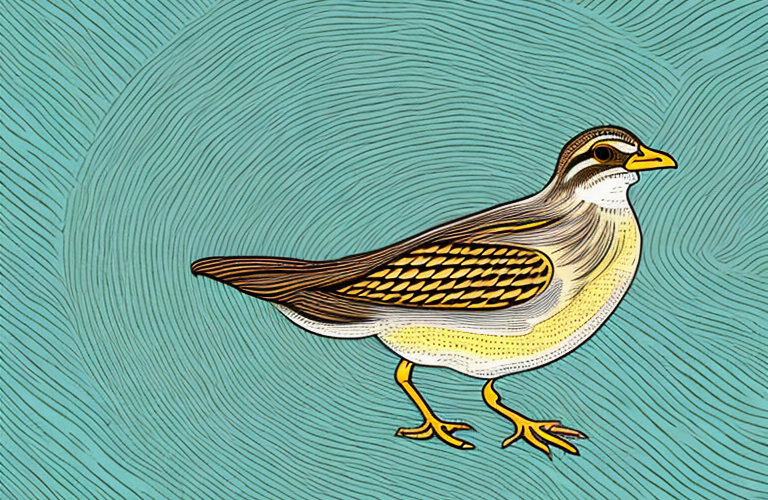
Physical Characteristics of the Corn Crake
The Corn Crake measures around 25 to 27 centimeters in length and has a wingspan ranging from 40 to 44 centimeters. It has a plump body with a buff-brown plumage that blends seamlessly with its environment. The male and female Corn Crakes look similar, displaying no significant differences in their appearance. However, juveniles often exhibit more scattered markings on their feathers until they reach maturity.
This bird’s most distinctive feature is its bright red bill, which contrasts with its muted plumage. The Corn Crake’s bill is adapted for foraging and probing the soil in search of insects and plant matter.
In terms of vocalizations, the Corn Crake is known for its loud and repetitive call, which serves as a territorial display and a means of communication between individuals. Its call is often heard during the breeding season, with males particularly active at night.
The Corn Crake is primarily found in grassy habitats, such as meadows, marshes, and wetlands. It prefers areas with dense vegetation, providing ample cover for nesting and foraging. This bird is known for its secretive nature, often hiding in tall grasses and using its cryptic plumage to blend in with its surroundings. The Corn Crake is a migratory species, spending the winter months in sub-Saharan Africa and returning to its breeding grounds in Europe and Asia during the summer.
Habitat and Distribution of the Corn Crake
The Corn Crake’s preferred habitat includes damp meadows, grasslands, marshes, and agricultural fields with tall vegetation. These areas provide cover and ample food sources for the Corn Crake, supporting their survival and successful breeding.
The distribution of the Corn Crake spans across Europe, Asia, and Africa. In Europe, it is prevalent in countries such as the United Kingdom, Ireland, Germany, Poland, and Ukraine. In Asia, it can be found in Siberia, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. In Africa, the Corn Crake is seen in countries like Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, and Egypt, among others.
During the breeding season, Corn Crakes migrate to their respective breeding grounds, while in winter, they undertake a long journey to sub-Saharan Africa, seeking warmer climates and abundant food sources.
The Corn Crake is a secretive bird that is known for its distinctive call, which sounds like a rasping “crex crex.” This call is most commonly heard during the breeding season, as males use it to attract females and establish their territory. The Corn Crake’s call is so loud that it can be heard up to 1 kilometer away, making it an important part of their breeding behavior.
Life Cycle and Reproduction of the Corn Crake
The breeding season for the Corn Crake typically begins in late April and lasts until August. Monogamous in nature, this bird constructs its nest on the ground, often hidden amidst dense vegetation. The female Corn Crake lays a clutch of 8 to 12 eggs, which she incubates for approximately 17 to 21 days.
Once the eggs hatch, both the male and female actively participate in caring for the offspring. They provide food and protection, ensuring the chicks grow and develop successfully. The young Corn Crakes fledge after around 20 to 24 days and become independent shortly after.
The Corn Crake reaches sexual maturity at the age of one year, and the breeding cycle continues as these birds maintain their populations.
During the breeding season, male Corn Crakes establish territories and engage in vocal displays to attract females. Their distinctive call, a repetitive “crex crex,” can be heard throughout the night. This vocalization is essential for communication and mate selection.
After the breeding season, Corn Crakes undergo a period of migration. They leave their breeding grounds in Europe and travel south to spend the winter in sub-Saharan Africa. This long-distance migration is necessary to find suitable feeding and wintering habitats.
Diet and Feeding Habits of the Corn Crake
The Corn Crake primarily feeds on a diverse diet that includes insects, snails, worms, spiders, small mammals, seeds, and various types of vegetation. Its bill is perfectly adapted for probing the soil and vegetation, allowing the bird to forage efficiently and extract food sources from the ground.
During the breeding season, when protein-rich food is crucial for the growing chicks, the Corn Crake’s diet consists mainly of insects. As the season progresses, it gradually shifts towards a more herbivorous diet, incorporating an assortment of seeds and plants.
The Corn Crake’s feeding behavior is primarily crepuscular and nocturnal, as it is more active during the twilight hours and prefers to forage under the cover of darkness to reduce the risk of predation.
In addition to its diverse diet, the Corn Crake also has a unique feeding behavior known as “leaf flipping.” This behavior involves the bird flipping over leaves and other vegetation to uncover hidden insects and invertebrates. By using this technique, the Corn Crake is able to access food sources that may be concealed from other foraging birds.
Behavior and Vocalizations of the Corn Crake
The Corn Crake is known for its secretive behavior, often relying on its excellent camouflage to remain hidden in its habitat. This bird is not known for its flying abilities and tends to walk or run within its environment, making quick dashes to cover when threatened.
In terms of vocalizations, as mentioned earlier, the Corn Crake emits a distinctive rasping call during the breeding season. This call is primarily used to establish territories and attract mates.
Interestingly, the Corn Crake has a unique behavior of “rattling,” where it briefly spreads its wings and produces a peculiar vibrating sound. This behavior is thought to be associated with territorialism or courtship rituals.
Another interesting behavior of the Corn Crake is its ability to mimic other bird species. This mimicry is most commonly observed in males during the breeding season, as they use it as a way to attract females and establish dominance. The Corn Crake’s mimicry skills are so impressive that it can accurately imitate the calls of various bird species, fooling both other birds and human observers.
Conservation Status and Threats to the Corn Crake Population
The Corn Crake is classified as a species of conservation concern due to a significant decline in its population over the past several decades. The threats faced by the Corn Crake include habitat loss, changes in agriculture practices, intensified land use, and the loss of suitable nesting sites.
The conversion of grasslands and meadows into agricultural fields, as well as the removal of hedgerows, significantly impacts the Corn Crake’s habitat and reduces its available foraging areas. Additionally, the increased use of pesticides and herbicides reduces the availability of insect prey, which is vital for the bird’s survival.
Furthermore, the loss of wetlands, drainage of marshes, and the creation of drainage ditches disrupt the Corn Crake’s breeding grounds, leading to further declines in populations.
To address these threats, a concerted effort is required to protect and restore the Corn Crake’s habitats and implement sustainable land management practices that can support the species’ populations.
One of the key factors contributing to the decline of the Corn Crake population is the fragmentation of its habitat. As human activities continue to encroach upon natural areas, the Corn Crake’s breeding and foraging grounds become increasingly isolated. This fragmentation limits the bird’s ability to find suitable mates and resources, further exacerbating the population decline.
In addition to habitat loss, climate change poses a significant threat to the Corn Crake population. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can disrupt the bird’s breeding and migration cycles. For example, earlier springs may cause the Corn Crake to arrive at its breeding grounds before suitable nesting sites are available, leading to breeding failures. Similarly, extreme weather events such as storms and droughts can destroy nests and reduce the availability of food sources.
Importance of the Corn Crake in Ecosystems
The Corn Crake plays a crucial role in ecosystems where it inhabits. As an insectivorous bird, it helps control populations of insects and other invertebrates, maintaining a balance in local ecosystems. Additionally, as the Corn Crake feeds on seeds and vegetation, it assists in seed dispersal, facilitating the regeneration of plant species within its habitats.
Moreover, the presence of the Corn Crake serves as an indicator of the environmental health of grasslands and wetlands. By monitoring the population trends of this species, conservationists can identify potential issues and implement measures to preserve biodiversity and ecosystem integrity.
Furthermore, the Corn Crake’s unique vocalizations have cultural significance in many regions. Its distinctive call, often described as a rasping sound, is a familiar sound in rural areas and is deeply rooted in local folklore and traditions. The bird’s presence and its call are often associated with the arrival of spring and are celebrated in festivals and songs.
In addition to its ecological and cultural importance, the Corn Crake also contributes to the economy in certain regions. Birdwatching and ecotourism activities centered around the observation of this elusive bird attract visitors from around the world. These tourists not only provide economic benefits to local communities but also raise awareness about the importance of conserving the Corn Crake’s habitats and the broader ecosystems they support.
Interesting Facts About the Corn Crake
Here are some interesting facts about the Corn Crake:
- The Corn Crake is commonly referred to as the “landrail” due to its preference for rail-like habitats and its distinctive call.
- Despite being an accomplished runner, the Corn Crake’s flight is typically short and low, enabling it to cover short distances to move between suitable habitats.
- The population decline of the Corn Crake is often attributed to intensive farming practices and the loss of traditional hay meadows.
- Female Corn Crakes are known for their adeptness in hiding their nests, making them incredibly difficult to locate.
- The call of the Corn Crake has cultural significance in various regions, being associated with the arrival of spring or considered a sign of good luck.
The Corn Crake is a migratory bird that breeds in Europe and Asia, and winters in sub-Saharan Africa. It undertakes long-distance migrations, covering thousands of kilometers each year.
During the breeding season, male Corn Crakes are known for their distinctive call, which is often described as a repetitive “crex crex” sound. This call is used to attract females and establish territories.
How to Identify and Differentiate the Corn Crake from Similar Bird Species
Identifying the Corn Crake can be challenging, especially as it shares some similarities with other bird species. However, a few distinguishing characteristics can help differentiate the Corn Crake:
- The Corn Crake has a buff-brown plumage that blends with its grassy habitat, making it difficult to spot. Its bright red bill stands out against its muted colors.
- When observing the Corn Crake in flight, its short and low flight pattern is noticeable, distinguishing it from other birds with more powerful flight capabilities.
- The Corn Crake’s distinct rasping call, resembling the sound of a corn saw, is a vital clue for identifying this species.
In addition to these physical characteristics, the Corn Crake also has specific behaviors that can aid in its identification. One such behavior is its preference for hiding in dense vegetation, particularly during the breeding season. This secretive behavior can make it even more challenging to spot the Corn Crake in its natural habitat.
Conservation Efforts for Protecting the Corn Crake’s Habitat
Conservation organizations and governmental bodies are actively engaged in efforts to protect the Corn Crake and its habitat. These initiatives focus on implementing measures such as:
- Designating protected areas and creating nature reserves specifically for the Corn Crake and other threatened bird species.
- Implementing sustainable land management practices, including agri-environment schemes that support the Corn Crake’s habitat and promote biodiversity.
- Restoring wetlands, grasslands, and meadows to provide suitable breeding and foraging grounds for the Corn Crake.
- Supporting research and monitoring programs to gather data on Corn Crake populations, movements, and habitat requirements.
In addition to these measures, conservation efforts also involve raising awareness among local communities and stakeholders about the importance of protecting the Corn Crake’s habitat. This includes educational campaigns, workshops, and outreach programs that aim to foster a sense of stewardship and encourage sustainable practices in the surrounding areas.
Tips for Birdwatching and Spotting a Corn Crake in the Wild
Spotting a Corn Crake in the wild requires patience, keen observation skills, and knowledge of its habitat preferences. Here are some tips for birdwatching and increasing your chances of spotting a Corn Crake:
- Visit wetlands, meadows, or grasslands with tall vegetation during the breeding season, as this is when Corn Crakes are most active and vocal.
- Arrive early in the morning or during dusk, when the Corn Crake is more likely to be calling or foraging.
- Listen for the distinctive rasping call, and use it as a guide to locate and identify the Corn Crake’s hiding spot.
- Be patient and scan the surroundings carefully, as the Corn Crake’s camouflage can make it difficult to spot. Look for any subtle movements or quick dashes to cover.
- Binoculars are essential for observing details such as the bird’s red bill or any unique behaviors like wing rattling.
Another helpful tip for spotting a Corn Crake is to familiarize yourself with its preferred habitat. Corn Crakes are often found in areas with dense vegetation, such as overgrown fields or marshy grasslands. Look for areas with tall grasses or reeds, as these provide ideal hiding spots for the bird.
In addition, learning about the Corn Crake’s behavior can greatly increase your chances of spotting one. These birds are known to be secretive and elusive, often staying hidden in the vegetation. However, they may occasionally venture out into more open areas to forage for food. Keep an eye out for any movement or rustling in the grass, as this could indicate the presence of a Corn Crake.
The Role of Citizen Science in Monitoring Corn Crake Populations
Citizen science initiatives have proven invaluable in monitoring Corn Crake populations and gathering data on their distribution and trends. Volunteers, birdwatchers, and local communities contribute to these efforts by participating in surveys, submitting sightings, and assisting in conservation projects.
Through citizen science, it is possible to gather widespread data on the presence and abundance of Corn Crakes in various habitats. This information aids in identifying vital feeding and breeding areas, assessing population trends, and developing effective conservation strategies to protect the Corn Crake and its habitat.
In addition to monitoring population numbers and distribution, citizen science also plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior and ecology of Corn Crakes. By observing their feeding habits, mating rituals, and nesting behaviors, researchers can gain valuable insights into the species’ life cycle and habitat requirements.
Challenges Faced by Conservationists in Preserving the Corn Crake’s Population
Conservationists face several challenges in safeguarding the Corn Crake’s population and ensuring its long-term survival:
- Habitat loss and degradation due to changing agricultural practices and urbanization pose significant threats to the Corn Crake’s survival.
- Securing sufficient funding and resources for habitat restoration projects, research, and monitoring programs is often a challenge.
- The secretive nature of the Corn Crake makes it challenging to gather accurate population data and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
- Addressing conflicts between conservation goals and the needs of farmers or landowners requires careful collaboration and the development of sustainable land management practices.
Success Stories: Examples of Successful Conservation Initiatives for the Corn Crake
Amidst the various challenges, several conservation initiatives have shown promising results in protecting the Corn Crake:
- In the United Kingdom, the RSPB (Royal Society for the Protection of Birds) manages nature reserves specifically tailored to support breeding Corn Crakes and other endangered bird species. These reserves offer suitable habitats, safe nesting areas, and ample food sources.
- In Belarus, a country known for hosting a significant Corn Crake population, the government has implemented a range of measures, including designating nature reserves and promoting agri-environmental schemes that support the species’ habitat requirements.
- Collaborative efforts between conservation organizations, farmers, and local communities in Ireland have successfully preserved and restored grasslands, benefiting the Corn Crake and other threatened bird species.
These success stories highlight the importance of targeted conservation efforts, cooperation between stakeholders, and sustainable land management practices in ensuring the survival of the Corn Crake.
Future Outlook for the Conservation of the Corn Crake
The future of the Corn Crake remains uncertain, given the ongoing threats to its population and habitat. However, there is optimism that continued conservation efforts, public awareness campaigns, and policy changes can positively impact the species.
By striving towards sustainable land management practices, protecting and restoring critical habitats, and incorporating the findings of ongoing research, it is possible to mitigate the risks faced by the Corn Crake and ensure its long-term survival. Public participation through citizen science and support for conservation organizations play a crucial role in safeguarding this remarkable bird for future generations to appreciate and cherish.