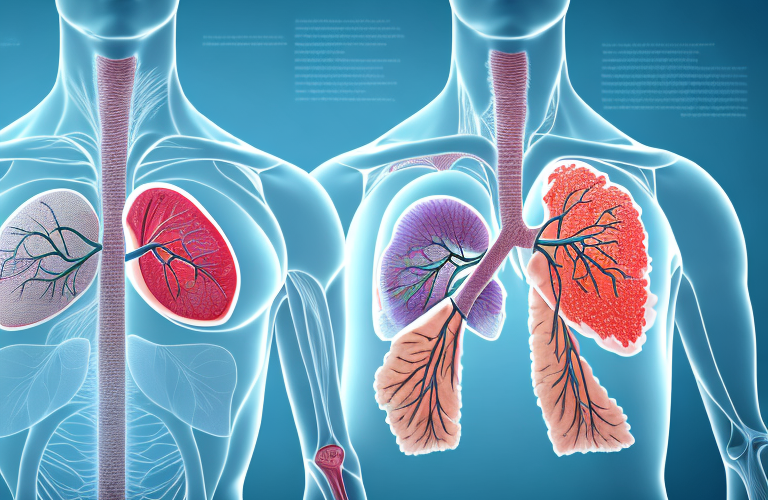
The respiratory system is responsible for transporting oxygen from the air to the body’s tissues and removing carbon dioxide. The lungs are the central organ of the respiratory system, and play a critical role in keeping us alive. Understanding the anatomy and function of the lungs is critical to maintaining optimal lung health, especially in the face of increasing levels of pollutants and respiratory diseases. Here’s what you need to know about the lungs, their anatomy and function, lung health, and common lung disorders to maintain optimal respiratory health.
Understanding the Respiratory System: How the Lungs Work
The lungs work like two large bags. Air comes in through the nose and mouth, goes through the trachea, and gets into the bronchial tubes – a set of tubes that branch out into smaller and smaller tubes – until it reaches the alveoli – tiny sacs found at the end of each bronchiole. Oxygen from the air diffuses through the lining of the alveoli and into the capillaries that surround them, while carbon dioxide moves from the capillaries into the alveoli to be exhaled out of the body.
In addition to their role in respiration, the lungs also play a crucial role in the immune system. They contain specialized cells that help to identify and remove harmful substances, such as bacteria and viruses, from the body. These cells work together with other components of the immune system, such as antibodies and white blood cells, to protect the body from infection and disease.
However, the lungs are also vulnerable to damage from environmental factors, such as air pollution and smoking. Exposure to these harmful substances can lead to inflammation, scarring, and other respiratory problems. It is important to take steps to protect your lungs, such as avoiding smoking and minimizing exposure to air pollution, in order to maintain good respiratory health.
The Anatomy of the Lungs: A Detailed Look
The lungs are divided into lobes – the left lung has two lobes, while the right lung has three. There are also smaller sections within the lobes called bronchopulmonary segments, which are separated by connective tissue. Inside each bronchopulmonary segment, there are many tiny air sacs called alveoli that allow for gas exchange to occur. The airways leading up to the alveoli are known as bronchioles. In between the alveoli are tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are responsible for exchanging gases and nutrients with the surrounding tissues. Surrounding the lungs is a thin membrane called the pleura, which helps keep the lungs in place and protects them as they move during breathing.
The lungs are also responsible for producing a substance called surfactant, which helps to reduce surface tension within the alveoli. This allows the alveoli to expand and contract more easily during breathing. Additionally, the lungs play a crucial role in regulating the body’s pH balance by removing excess carbon dioxide from the bloodstream. This process, known as ventilation, helps to maintain a healthy balance of acids and bases in the body. Without proper ventilation, the body can become too acidic, leading to a condition known as respiratory acidosis.
What are Alveoli and How do They Function in Gas Exchange?
Alveoli are tiny air sacs that make up the bulk of the lungs. They are the site of gas exchange, where oxygen from inhaled air diffuses across the alveolar-capillary membrane and into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide from the bloodstream diffuses across the membrane and into the alveoli to be exhaled. Having a large surface area of alveoli is crucial to optimize gas exchange and maintain proper oxygenation levels in the body.
Alveoli are surrounded by a network of capillaries, which are small blood vessels that allow for the exchange of gases between the lungs and the rest of the body. The oxygen-rich blood that leaves the alveoli through the capillaries is then transported to the heart, where it is pumped to the rest of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide-rich blood from the body is transported to the lungs through the capillaries, where it is then exhaled through the alveoli. This process of gas exchange is essential for maintaining the body’s pH balance and ensuring that all organs receive the oxygen they need to function properly.
The Significance of Lung Capacity and Volume
Lung capacity and volume refer to the amount of air that can be breathed in or out during different phases of the respiratory cycle. Maximum lung capacity is achieved during a deep inhalation (called inspiratory capacity), while minimum lung capacity is reached during a deep exhalation (called expiratory reserve volume). These measurements are useful in diagnosing and tracking respiratory disorders like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which can lead to decreased lung volume and capacity.
In addition to respiratory disorders, lung capacity and volume can also be affected by lifestyle factors such as smoking, pollution, and physical activity. Smoking can cause damage to the lungs and decrease lung capacity, while regular exercise can improve lung function and increase lung capacity. Additionally, exposure to air pollution can lead to respiratory problems and decreased lung function over time.
Breathing Techniques for a Healthy Respiratory System
Proper breathing techniques can help increase lung capacity, reduce anxiety, and improve overall respiratory health. Techniques such as deep breathing, pursed lip breathing, and diaphragmatic breathing have all been shown to improve lung function, reduce symptoms of respiratory disorders, and increase oxygenation levels. Additionally, regular exercise and maintenance of good posture can also help strengthen the respiratory muscles and promote proper breathing.
Another breathing technique that can be beneficial for respiratory health is alternate nostril breathing. This technique involves closing one nostril with a finger and inhaling through the other nostril, then switching and exhaling through the opposite nostril. This technique has been shown to improve lung function and reduce stress levels.
In addition to breathing techniques, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle to support respiratory health. This includes avoiding smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, as well as minimizing exposure to air pollution and other environmental irritants. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can also provide important nutrients to support respiratory function.
Common Lung Disorders: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
There are several common lung disorders that can impact lung function, including asthma, COPD, pneumonia, and lung cancer. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways, while COPD is a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation due to inflammation and destruction of lung tissue. Pneumonia is an acute respiratory disorder caused by an infection in the lungs, and lung cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the lung tissue. Treatment options for these disorders vary, but may include medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery.
It is important to note that smoking is a major risk factor for many lung disorders, including COPD and lung cancer. Quitting smoking can greatly reduce the risk of developing these conditions and can also improve lung function in those who already have them. Additionally, regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can also help improve lung function and reduce the risk of developing lung disorders.
Smoking and Lung Health: The Risks and Consequences
Smoking is a leading cause of lung disease and has been linked to a variety of respiratory problems, including lung cancer and COPD. Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage the alveoli and other lung tissue, leading to decreased lung capacity and other respiratory problems. Quitting smoking is the single most effective way to reduce the risk of developing lung disease, as well as many other health problems.
In addition to the negative effects on lung health, smoking can also have a significant impact on overall cardiovascular health. Smoking increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of blood vessels, leading to a buildup of plaque and narrowing of the arteries. This can ultimately result in reduced blood flow to vital organs, including the heart and brain. Quitting smoking can help to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of these serious health problems.
Maintaining Healthy Lungs: Diet, Exercise and Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is key to preventing lung disease and promoting optimal lung health. Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables, staying physically active, and avoiding environmental pollutants can all help promote lung health and reduce the risk of respiratory problems. Additionally, maintaining good hand hygiene and getting regular vaccinations, like the flu and pneumonia vaccine, can also help keep the respiratory system healthy.
Another important factor in maintaining healthy lungs is avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke. Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Quitting smoking can significantly improve lung function and reduce the risk of developing lung disease. It is also important to avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, which can be just as harmful as smoking itself.
In addition to diet and exercise, practicing good breathing techniques can also help improve lung health. Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help strengthen the muscles used for breathing and improve lung capacity. Yoga and meditation can also be beneficial for improving breathing and reducing stress, which can have a positive impact on lung health.
How to Improve Indoor Air Quality for Better Lung Health
Indoor air quality can have a significant impact on respiratory health. Common indoor pollutants like tobacco smoke, mold, and pesticides can all have deleterious effects on lung function, and may increase the risk of respiratory problems. Maintaining a clean living environment, using an air purification system, and avoiding smoking indoors can all help improve indoor air quality and promote optimal respiratory health.
In addition to these measures, it is also important to regularly change air filters in your home’s heating and cooling system. Dirty filters can circulate pollutants and allergens throughout your home, worsening indoor air quality. It is recommended to change filters every three months, or more frequently if you have pets or allergies. Another way to improve indoor air quality is to increase ventilation by opening windows or using exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens. This can help remove pollutants and bring in fresh air.
Innovative Treatments for Lung Cancer and Other Diseases
Advancements in medical technologies and treatments have resulted in new and innovative treatments for a variety of respiratory disorders, including lung cancer and COPD. Treatments like minimally-invasive surgeries, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy have all been shown to be effective in treating a range of respiratory disorders and improving respiratory function. Additionally, many clinical trials are currently underway to explore new and promising treatments that could revolutionize the field of respiratory medicine.
One promising area of research is the use of gene therapy to treat lung cancer. This involves modifying a patient’s genes to target and destroy cancer cells, while leaving healthy cells unharmed. While still in the early stages of development, early results have been promising and suggest that gene therapy could become a powerful tool in the fight against lung cancer.
Another area of focus is the development of personalized medicine for respiratory disorders. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup and other factors, doctors can tailor treatments to the individual, increasing the chances of success and reducing the risk of side effects. This approach has already shown promise in the treatment of lung cancer and other respiratory disorders, and is likely to become more widespread in the coming years.
Understanding Asthma: Triggers, Symptoms and Management Tips
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Common symptoms of asthma include wheezing, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, and coughing. Asthma triggers can include allergens, pollutants, exercise, and stress. Managing asthma involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes, including avoiding triggers, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring symptoms to prevent exacerbations.
It is important for individuals with asthma to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an asthma action plan. This plan outlines steps to take when symptoms worsen, including when to seek emergency medical care. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help ensure that asthma is well-controlled and that medication dosages are appropriate.
In addition to medication and lifestyle changes, alternative therapies such as breathing exercises, acupuncture, and herbal remedies may also be helpful for some individuals with asthma. However, it is important to discuss these options with a healthcare provider before trying them, as they may interact with prescribed medications or worsen symptoms in some cases.
Pneumonia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that affects the lungs and can be caused by a variety of different pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Symptoms of pneumonia can include fever, cough, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Diagnosis involves a physical exam, chest x-ray, and sometimes a sputum culture. Treatment typically involves antibiotics or antiviral medication, rest, and supportive care.
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing pneumonia. These include being over the age of 65, having a weakened immune system, smoking, and having underlying medical conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is important to take steps to reduce your risk of pneumonia, such as getting vaccinated against the flu and pneumococcal bacteria, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick.
In some cases, pneumonia can lead to complications such as sepsis, respiratory failure, or lung abscesses. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of pneumonia, especially if you are in a high-risk group. Your healthcare provider can help determine the best course of treatment and monitor you for any potential complications.
The Role of Genetics in Lung Health
Research has shown that genetics can play a role in the development and progression of respiratory diseases like COPD and lung cancer. Identifying genetic risk factors for these diseases can help clinicians better understand the disease, predict disease progression, and develop personalized treatment plans. Additionally, genetic testing may also be used to identify individuals who are at increased risk of developing respiratory disorders, potentially allowing for early intervention and prevention.
Recent studies have also suggested that genetics may influence an individual’s response to certain medications used to treat respiratory diseases. For example, some genetic variations have been linked to increased risk of adverse reactions to certain medications, while others may affect how well a medication works. By understanding an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to maximize effectiveness and minimize potential side effects.
Importance of Early Screening for Lung Diseases
Early screening and detection of respiratory diseases can lead to earlier diagnosis, treatment, and improved outcomes. Routine screening for lung cancer, for example, can help identify tumors at an earlier stage when treatment is more likely to be successful. Additionally, early detection and management of respiratory disorders like COPD and asthma can help prevent exacerbations and limit disease progression.
In conclusion, understanding the anatomy and function of the lungs is critical for maintaining optimal respiratory health. Lung capacity, proper breathing techniques, and lifestyle modifications can all help promote lung health and reduce the risk of respiratory disease. Furthermore, early detection and treatment of respiratory disorders are vital in optimizing treatment outcomes and promoting overall respiratory health.
It is important to note that certain populations may be at higher risk for developing respiratory diseases and may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening. For example, individuals with a history of smoking, exposure to environmental pollutants, or a family history of lung cancer may be at increased risk for developing respiratory diseases. Additionally, older adults and those with pre-existing respiratory conditions may also benefit from more frequent screening and monitoring.