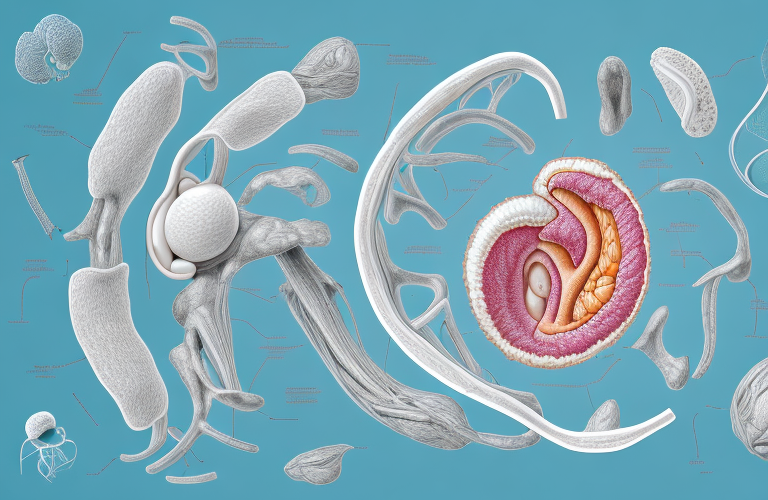
The uterus, also known as the womb, is a vital organ in the female reproductive system. It plays a crucial role in pregnancy and childbirth, but it also has other functions that are important for women’s health. In this article, we will delve deep into the function, anatomy and other aspects of the uterus, so let’s get started!
Understanding the Function of the Uterus
The main function of the uterus is to provide a safe and nurturing environment for a fertilized egg to develop into a fetus. During the menstrual cycle, the uterus thickens its lining in preparation for a potential pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg implants into the lining and begins to grow. The uterus then supplies nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus until it is ready for birth.
However, if fertilization does not occur, the uterus sheds its lining during menstruation. This process is regulated by hormones, specifically estrogen and progesterone, which are produced by the ovaries. The uterus also plays a role in sexual pleasure, as it can contract during orgasm.
In addition to its reproductive functions, the uterus also plays a role in the immune system. It contains immune cells that help protect against infections and foreign substances. The uterus also produces cytokines, which are proteins that help regulate the immune response.
Furthermore, the uterus can be affected by various medical conditions, such as fibroids, endometriosis, and cancer. These conditions can cause pain, abnormal bleeding, and infertility. Treatment options may include medication, surgery, or a combination of both.
The Anatomy of the Uterus: A Comprehensive Overview
The uterus is a muscular organ that is approximately the size and shape of a pear. It is located in the pelvic cavity, between the bladder and the rectum. The uterus is composed of three layers: the innermost layer known as the endometrium, the middle layer known as the myometrium, and the outermost layer known as the perimetrium.
The endometrium is the thinnest layer and is shed during menstruation. The myometrium is the thickest layer and is responsible for the contractions that occur during labor and delivery. The perimetrium is the outermost layer that covers the uterus and helps to keep it in place.
The uterus is a vital reproductive organ in females and plays a crucial role in pregnancy. During pregnancy, the uterus expands to accommodate the growing fetus and contracts during labor to push the baby out of the birth canal. The uterus is also responsible for nourishing the developing fetus by providing it with oxygen and nutrients through the placenta.
Hormonal Regulation of the Uterus: How It Works
As mentioned earlier, the hormonal regulation of the uterus is critical for its proper function. Estrogen and progesterone are the two hormones responsible for regulating the menstrual cycle and preparing the uterus for pregnancy. Estrogen is responsible for thickening the uterus lining, while progesterone prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains the pregnancy.
However, an imbalance of these hormones can lead to various conditions, such as irregular periods, heavy bleeding, and infertility. These conditions can be managed through medication or other treatments, depending on the severity of the condition.
In addition to estrogen and progesterone, other hormones also play a role in the regulation of the uterus. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is produced by the hypothalamus and stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland. FSH and LH then stimulate the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone, which in turn regulate the uterus.
Furthermore, hormonal regulation of the uterus is not limited to the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Hormones also play a role in the development and function of the uterine lining, as well as in the contraction of the uterus during labor and delivery.
The Menstrual Cycle and the Role of the Uterus
The menstrual cycle is a complex process involving multiple organs and hormones. The uterus plays a vital role in this cycle, as it is responsible for shedding and regenerating its lining each month. The menstrual cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase, the ovulatory phase, and the luteal phase.
The follicular phase is the first phase of the menstrual cycle and starts on the first day of bleeding. The ovulatory phase occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels to the uterus. Finally, during the luteal phase, the uterus prepares for the arrival of a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the uterus sheds its lining and the menstrual cycle starts again.
It is important to note that the length and regularity of the menstrual cycle can vary from person to person. Factors such as stress, weight changes, and certain medical conditions can affect the menstrual cycle. It is recommended to track your menstrual cycle to better understand your body and identify any irregularities that may require medical attention.
Pregnancy and the Uterus: Changes and Adaptations
During pregnancy, the uterus undergoes various changes and adaptations to accommodate the growing fetus. It enlarges and stretches as the fetus grows, and the placenta, which is responsible for providing nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, attaches to the uterine wall. Hormonal changes also occur, as the levels of estrogen and progesterone increase to support the pregnancy.
However, some conditions can affect the uterus during pregnancy, such as preterm labor, preeclampsia, and placenta previa. These conditions can be managed through medication and close monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Another change that occurs in the uterus during pregnancy is the increase in blood flow. The blood vessels in the uterus expand to provide more blood to the growing fetus and placenta. This increased blood flow can also cause the uterus to feel heavier and more uncomfortable for the mother.
In addition, the uterus undergoes contractions during pregnancy, which can be a sign of preterm labor or Braxton Hicks contractions. These contractions help to prepare the uterus for labor and delivery, but if they occur too early, they can be a cause for concern and require medical attention.
Common Disorders and Conditions Affecting the Uterus
Various disorders and conditions can affect the uterus, ranging from benign to very serious. Some common disorders include endometriosis, fibroids, adenomyosis, and polyps. Endometriosis occurs when the endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, while fibroids are benign growths that develop in the uterus. Adenomyosis occurs when the endometrium grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, and polyps are abnormal growths that can develop in the uterus lining.
Other conditions that can affect the uterus include uterine prolapse, which occurs when the uterus drops into the vaginal canal, and uterine cancer, which is a malignant growth in the uterus. Symptoms of these conditions can include pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, and difficulty urinating. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms or have concerns about your reproductive health.
Endometriosis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Endometriosis is a painful condition that affects many women. It occurs when the endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus and can cause pelvic pain, infertility, and heavy periods. The cause of endometriosis is not well understood, but treatment options include medication, surgery, and alternative therapies such as acupuncture.
Recent studies have shown that endometriosis may also have a genetic component, with women who have a family history of the condition being more likely to develop it themselves. In addition, certain lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise may play a role in the development and management of endometriosis.
Fibroids: Types, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
Fibroids are benign tumors that develop in the uterus and can cause heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, and other symptoms. There are different types of fibroids, and treatment options include medication, surgery, and uterine fibroid embolization, which is a minimally invasive procedure that can shrink the fibroids.
It is important to note that not all fibroids require treatment. In some cases, fibroids may not cause any symptoms or may be small enough to not require intervention. However, regular monitoring is recommended to ensure that the fibroids do not grow or cause any complications. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and reducing stress may help manage symptoms and prevent the growth of fibroids.
Adenomyosis: Understanding this Painful Condition
Adenomyosis occurs when the endometrium grows into the muscular wall of the uterus and can cause pain and heavy bleeding. The cause of adenomyosis is not well understood, but treatment options include medication, surgery, and endometrial ablation.
Adenomyosis is a condition that primarily affects women in their 40s and 50s, but it can occur at any age. It is often misdiagnosed as uterine fibroids or endometriosis, which can delay proper treatment. Women with adenomyosis may experience symptoms such as severe menstrual cramps, pelvic pain, and pain during intercourse.
In addition to the traditional treatment options, some women have found relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and dietary changes. It is important for women with adenomyosis to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for their individual needs.
Polyps in the Uterus: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Polyps are abnormal growths that can develop in the uterus and can cause abnormal bleeding, pain, and other symptoms. Treatment options include monitoring, medication, and surgery, depending on the severity and location of the polyps.
It is important to note that polyps in the uterus are usually non-cancerous, but in rare cases, they can be cancerous. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or have concerns about polyps in your uterus.
Some risk factors for developing uterine polyps include obesity, high blood pressure, and taking certain medications such as tamoxifen. Additionally, women who have gone through menopause are at a higher risk for developing polyps.
Cancer of the Uterus: Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Cancer of the uterus is a potentially life-threatening condition that can affect women. Risk factors include age, obesity, and a history of certain conditions such as endometrial hyperplasia. Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular check-ups, and screening for cancer if necessary.
It is important to note that certain lifestyle factors may also increase the risk of developing cancer of the uterus. Smoking, for example, has been linked to an increased risk of this type of cancer. Additionally, women who have never been pregnant or who have a family history of uterine cancer may also be at higher risk. To reduce the risk of developing cancer of the uterus, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
Reproductive Health and Maintaining a Healthy Uterus
Maintaining good reproductive health is essential for women, and there are various ways to keep the uterus healthy. These include regular check-ups with healthcare professionals, practicing safe sex, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
In addition to these measures, it is important to be aware of any changes in your menstrual cycle or any unusual symptoms such as pain or abnormal bleeding. These could be signs of a potential issue with the uterus or reproductive system, and it is important to seek medical attention promptly. It is also recommended to avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can have negative effects on reproductive health.
Surgical Procedures Involving the Uterus: Risks and Benefits
Surgical procedures can be an effective way to treat various conditions involving the uterus. However, they also carry risks such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. It is important to discuss the risks and benefits with healthcare professionals before undergoing any surgery involving the uterus.
One common surgical procedure involving the uterus is a hysterectomy, which involves the removal of the uterus. This procedure is often recommended for conditions such as uterine fibroids, endometriosis, or cancer. While a hysterectomy can provide relief from symptoms and prevent the spread of cancer, it also means that a woman will no longer be able to become pregnant.
Another surgical procedure involving the uterus is a myomectomy, which involves the removal of uterine fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. This procedure is often recommended for women who want to preserve their fertility. However, a myomectomy can also carry risks such as scarring and the possibility of fibroids returning in the future.
Alternative Treatments for Uterine Disorders: What You Need to Know
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and yoga can be effective in managing various uterine disorders. However, it is essential to discuss these treatments with healthcare professionals before trying them, as they may interact with other medications and have side effects.
As you can see, the uterus is a complex and vital organ in the female reproductive system. Understanding its function, anatomy, and various conditions that can affect it is crucial for women’s health. By maintaining good reproductive health, getting regular check-ups, and seeking treatment when necessary, women can maintain a healthy uterus and overall wellbeing.
It is also important to note that alternative treatments should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical treatments. While they may provide relief from symptoms, they may not address the underlying cause of the uterine disorder. Therefore, it is crucial to work with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that includes both conventional and alternative therapies, if appropriate.